Learning Riemannian Metrics from Gravitational Waves
Ref Bari, Brown University

Advisor: Prof. Brendan Keith

Acknowledgements








Brendan Keith
Scott Field
Collin Capano
Michael Pürrer
Pranav Vinod
Morgan Beck






Acknowledgements



Neural ODE DynAMO
NSF Award 2407452
For Data-Driven Discovery of
Astrophysical Models and Orbits
Motivation


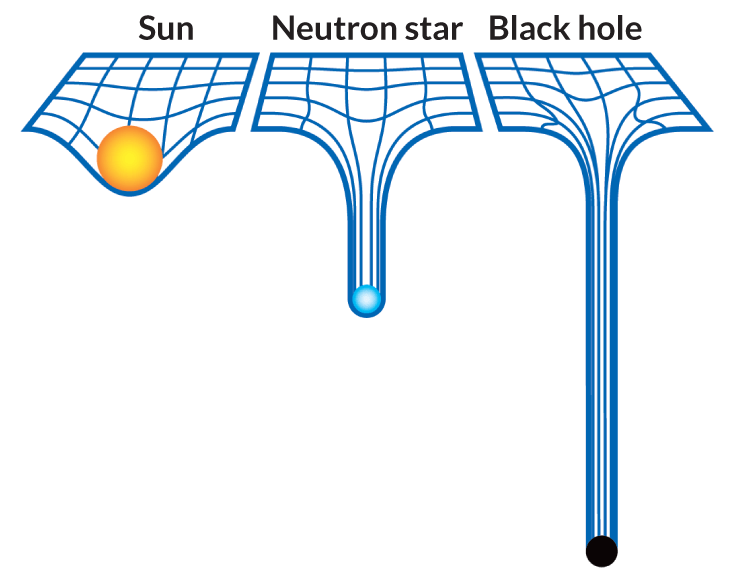
Motivation


Motivation


Event Horizon
Singularity
Motivation




The Inverse Problem
The Imaging Problem





Motivation


The Inverse Problem
The Imaging Problem




Motivation

for decisive contributions to the LIGO detector and the observation of gravitational waves
2017 Nobel Prize in Physics
Question


Answer







Summary
Conservative Dynamics: We created a NN which can learn solutions to Einstein's Field Equations (Schwarzschild Metric) from only gravitational waves
Dissipative Dynamics: NN can learn both conservative and dissipative dynamics of a binary black hole inspiral for the synthetic dissipation case.
Approach


The Forward Problem
The Inverse Problem


Approach


The Inverse Problem

The Forward Problem
Metric
Orbits
Waveforms
Approach


The Forward Problem
The Inverse Problem
Metric
Orbits
Waveforms
GENERIC Formalism
Einstein's Field Equations
GENERIC Formalism
GENERIC Formalism
GENERIC Formalism
Synthetic Dissipation
Simulated Dissipation
Birkhoff's Theorem
Ricci Tensor
Approach


The Forward Problem
The Inverse Problem


Approach


The Forward Problem
The Inverse Problem


Approach


The Forward Problem

The Inverse Problem



Forward Problem
The Inverse Problem
The Imaging Problem






Forward Problem
The Inverse Problem
The Imaging Problem






Forward Problem
The Inverse Problem
The Imaging Problem




The Forward Problem
Metric
Orbits
Waveforms
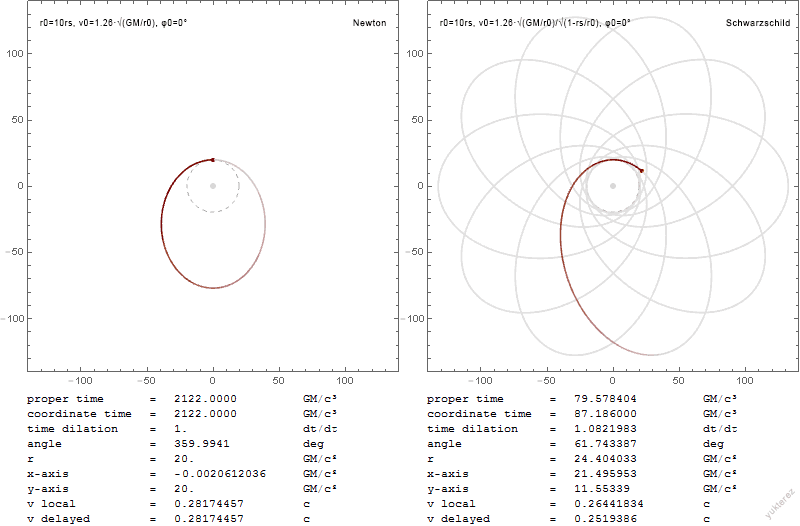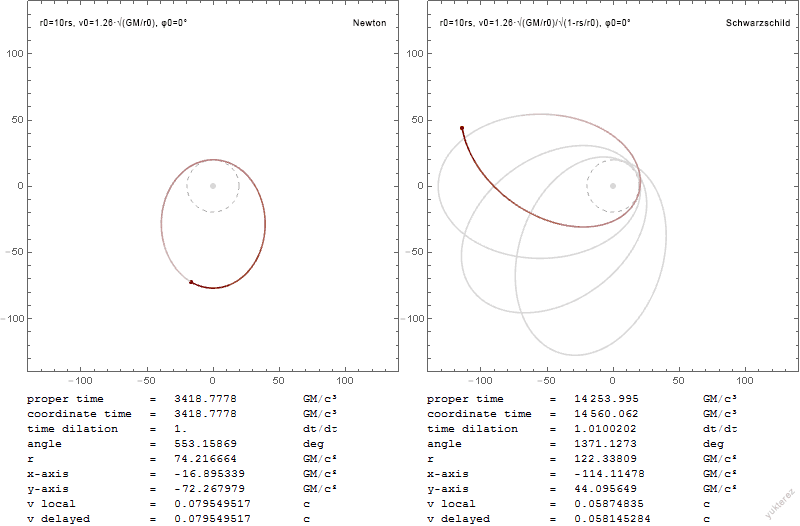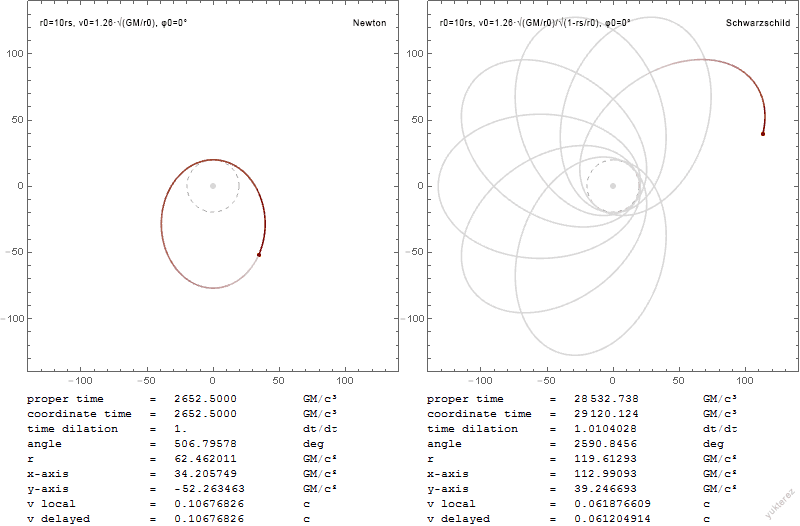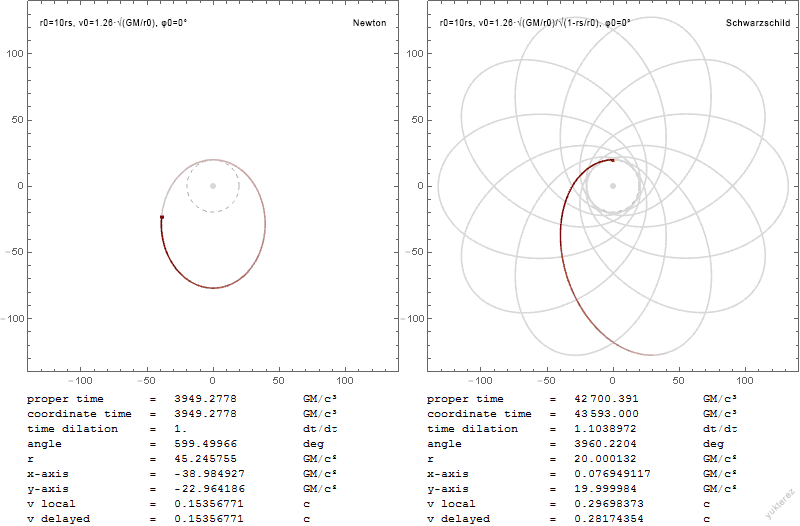
Credit: Wikipedia, Schwarzschild Geodesics


Forward Problem
The Inverse Problem
The Imaging Problem




The Forward Problem
Metric
Orbits
Waveforms

State Variables


Forward Problem
The Inverse Problem
The Imaging Problem




The Forward Problem
Metric
Orbits
Waveforms

Metric


Forward Problem
The Inverse Problem
The Imaging Problem




The Forward Problem
Metric
Orbits
Waveforms

Hamiltonian


Forward Problem
The Inverse Problem
The Imaging Problem




The Forward Problem
Metric
Orbits
Waveforms

Equations of Motion


Forward Problem
The Inverse Problem
The Imaging Problem




The Forward Problem
Metric
Orbits
Waveforms
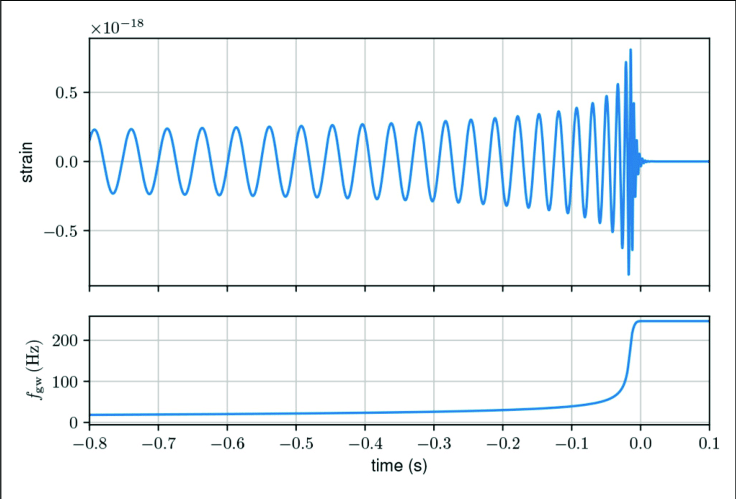
Gravitational Waveform


Forward Problem
The Inverse Problem
The Imaging Problem




The Forward Problem
Metric
Orbits
Waveforms
Schwarzschild Metric


Forward Problem
The Inverse Problem
The Imaging Problem




The Forward Problem
Metric
Orbits
Waveforms
Schwarzschild Metric


Forward Problem
The Inverse Problem
The Imaging Problem




The Forward Problem
Metric
Orbits
Waveforms
Schwarzschild Metric


Forward Problem
The Inverse Problem
The Imaging Problem




The Forward Problem
Metric
Orbits
Waveforms
Hamiltonian


Forward Problem
The Inverse Problem
The Imaging Problem




The Forward Problem
Metric
Orbits
Waveforms
Hamiltonian


Forward Problem
The Inverse Problem
The Imaging Problem




Hamiltonian Equations
The Forward Problem
Metric
Orbits
Waveforms


Forward Problem
The Inverse Problem
The Imaging Problem




The Forward Problem
Metric
Orbits
Waveforms
r Equations of Motion
Φ Equations of Motion


Forward Problem
The Inverse Problem
The Imaging Problem




The Forward Problem
Metric
Orbits
Waveforms


Forward Problem
The Inverse Problem
The Imaging Problem




The Forward Problem
Metric
Orbits
Waveforms


Forward Problem
The Inverse Problem
The Imaging Problem




The Forward Problem
Metric
Orbits
Waveforms


Forward Problem
The Inverse Problem
The Imaging Problem




The Forward Problem
Metric
Orbits
Waveforms
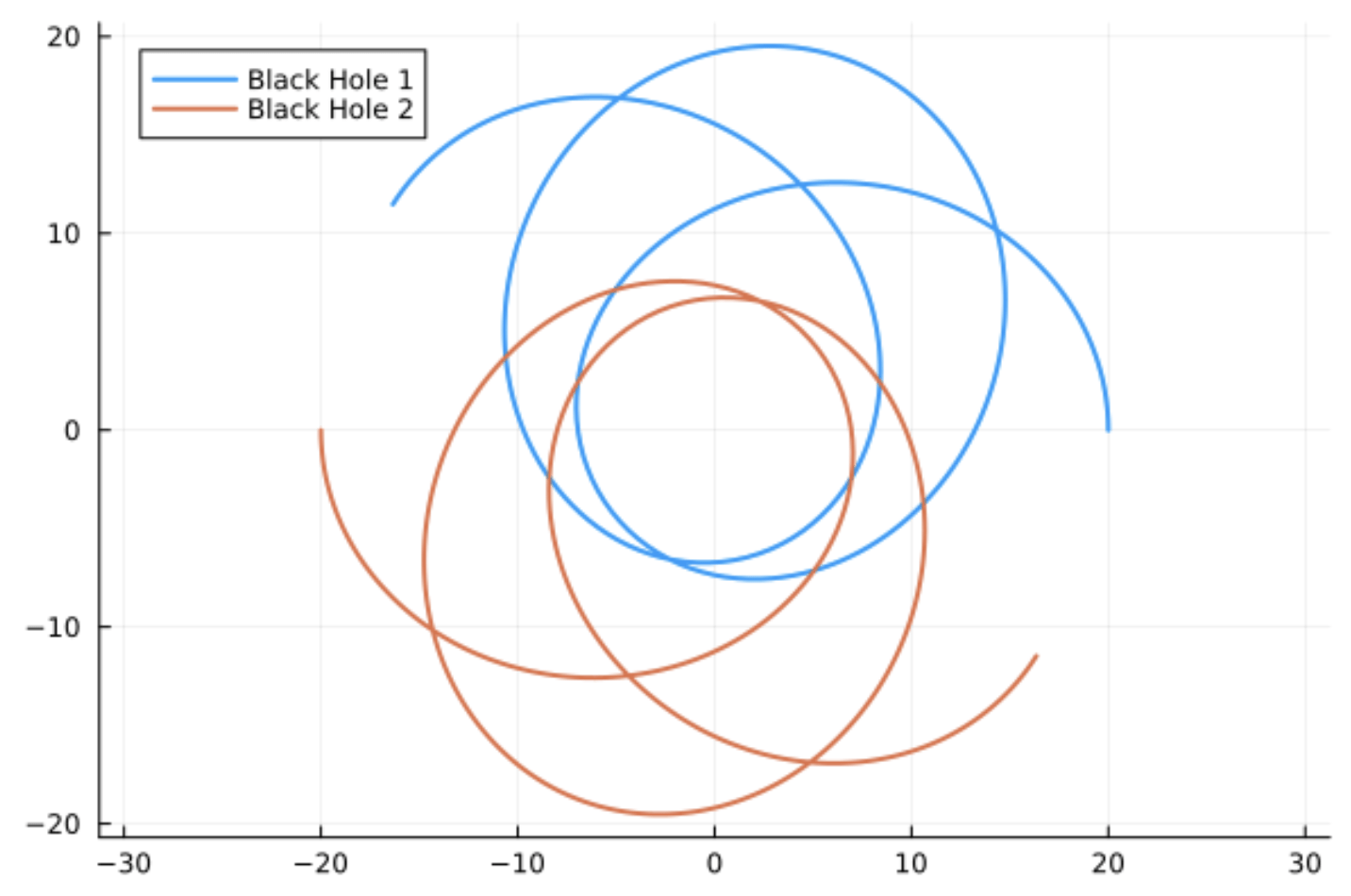


Forward Problem
The Inverse Problem
The Imaging Problem




The Forward Problem
Metric
Orbits
Waveforms
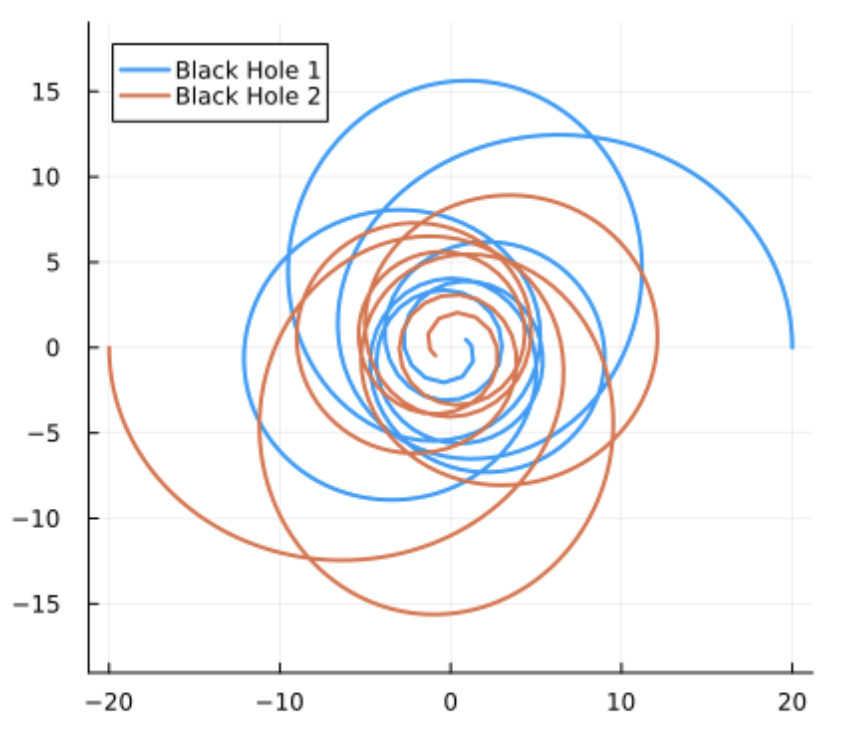
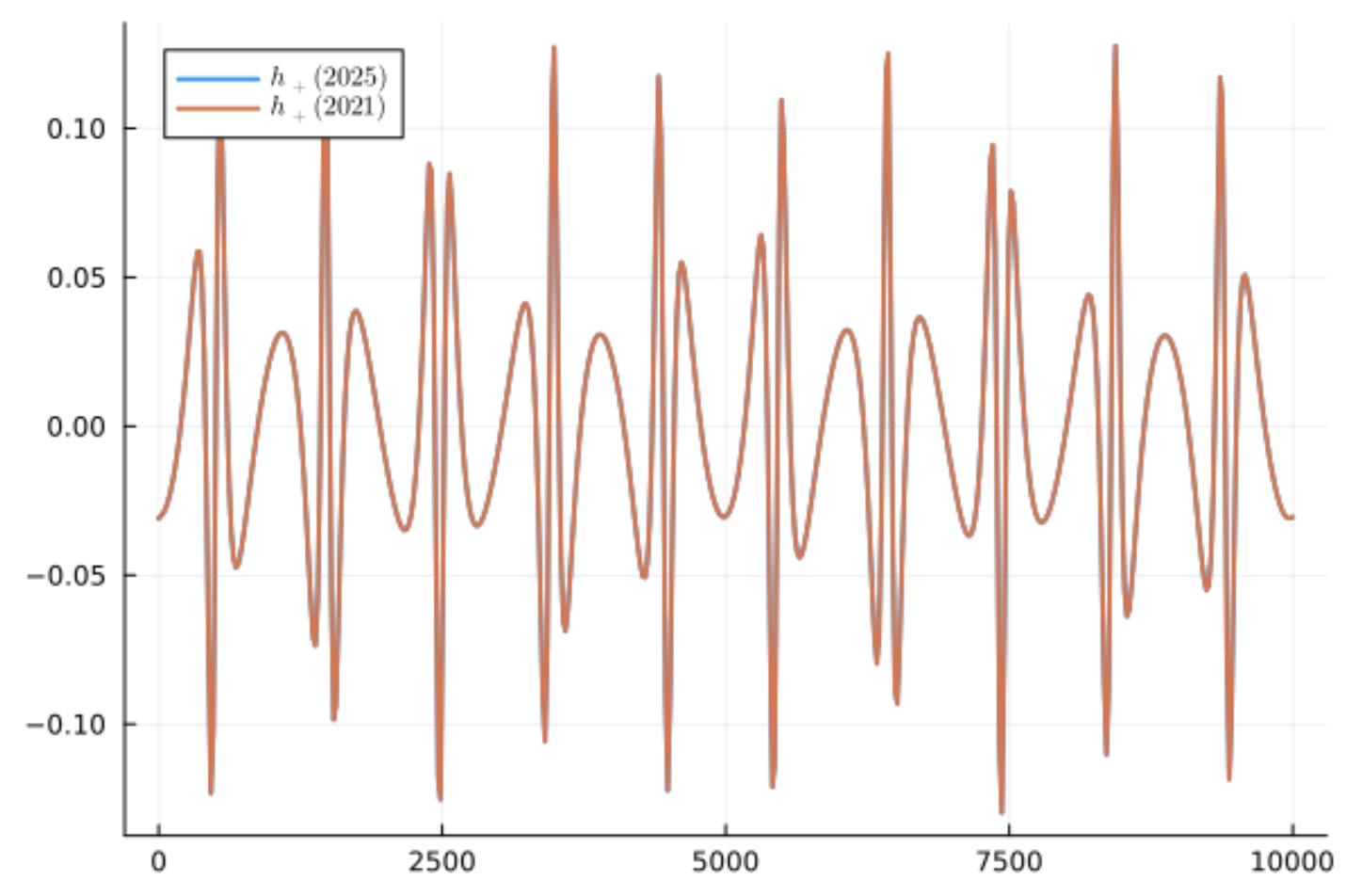
Angular Momentum Flux
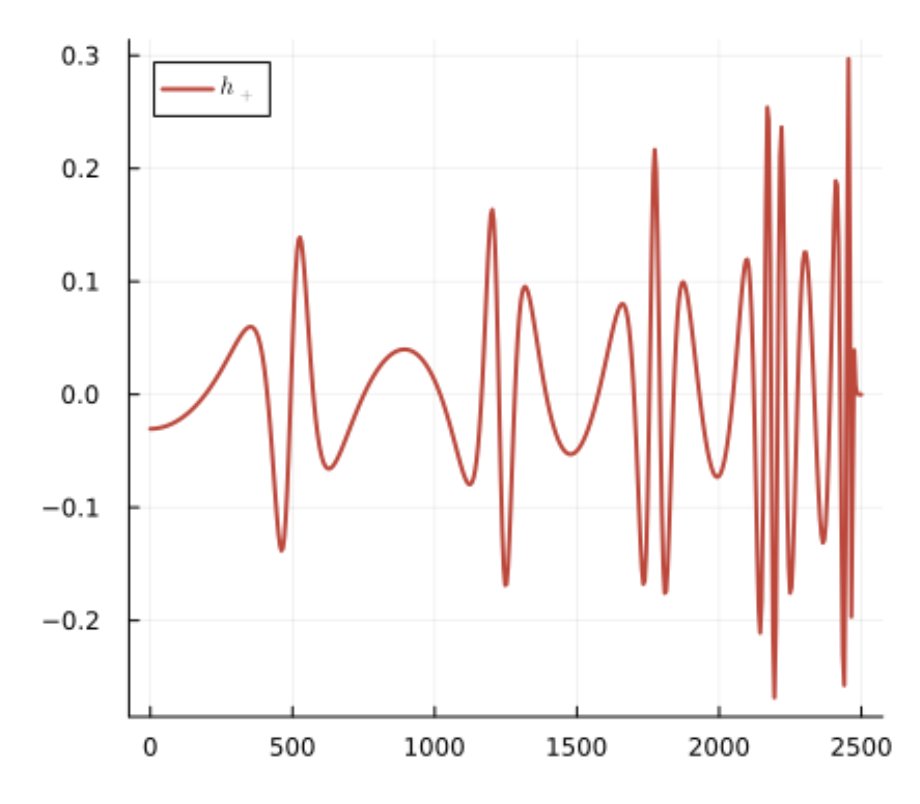

Forward Problem
The Inverse Problem
The Imaging Problem




Metric
Orbits
Waveforms

Conservative Dynamics


The Forward Problem
Dissipative Dynamics

Approach


The Forward Problem

The Inverse Problem

Approach


The Inverse Problem
GENERIC Formalism
Einstein's Field Equations
GENERIC Formalism
GENERIC Formalism
GENERIC Formalism
Synthetic Dissipation
Birkhoff's Theorem
Ricci Tensor

Approach


The Inverse Problem
GENERIC Formalism
Einstein's Field Equations
GENERIC Formalism
GENERIC Formalism
GENERIC Formalism
Synthetic Dissipation
Simulated Dissipation
Birkhoff's Theorem
Ricci Tensor
conservative
dissipative
Equilibrium Thermodynamics
Approach


The Inverse Problem
GENERIC Formalism
Einstein's Field Equations
GENERIC Formalism
GENERIC Formalism
GENERIC Formalism
Synthetic Dissipation
Simulated Dissipation
Birkhoff's Theorem
Ricci Tensor
conservative
dissipative
Equilibrium Thermodynamics
Approach


The Inverse Problem
GENERIC Formalism
Einstein's Field Equations
GENERIC Formalism
GENERIC Formalism
GENERIC Formalism
Synthetic Dissipation
Simulated Dissipation
Birkhoff's Theorem
Ricci Tensor
Inequilibrium Thermodynamics
conservative
dissipative
Approach


The Inverse Problem
GENERIC Formalism
Einstein's Field Equations
GENERIC Formalism
GENERIC Formalism
GENERIC Formalism
Synthetic Dissipation
Simulated Dissipation
Birkhoff's Theorem
Ricci Tensor
Inequilibrium Thermodynamics
conservative
dissipative
Approach


The Inverse Problem
GENERIC Formalism
Einstein's Field Equations
GENERIC Formalism
GENERIC Formalism
GENERIC Formalism
Synthetic Dissipation
Simulated Dissipation
Birkhoff's Theorem
Ricci Tensor
Inequilibrium Thermodynamics
conservative
dissipative
Approach


The Inverse Problem
GENERIC Formalism
Einstein's Field Equations
GENERIC Formalism
GENERIC Formalism
GENERIC Formalism
Synthetic Dissipation
Simulated Dissipation
Birkhoff's Theorem
Ricci Tensor
Inequilibrium Thermodynamics
conservative
dissipative
Approach


The Inverse Problem
GENERIC Formalism
Einstein's Field Equations
GENERIC Formalism
GENERIC Formalism
GENERIC Formalism
Synthetic Dissipation
Simulated Dissipation
Birkhoff's Theorem
Ricci Tensor
Approach


The Inverse Problem
GENERIC Formalism
Einstein's Field Equations
GENERIC Formalism
GENERIC Formalism
GENERIC Formalism
Synthetic Dissipation
Simulated Dissipation
Birkhoff's Theorem
Ricci Tensor
Approach


The Inverse Problem
GENERIC Formalism
Einstein's Field Equations
GENERIC Formalism
GENERIC Formalism
GENERIC Formalism
Synthetic Dissipation
Simulated Dissipation
Birkhoff's Theorem
Ricci Tensor
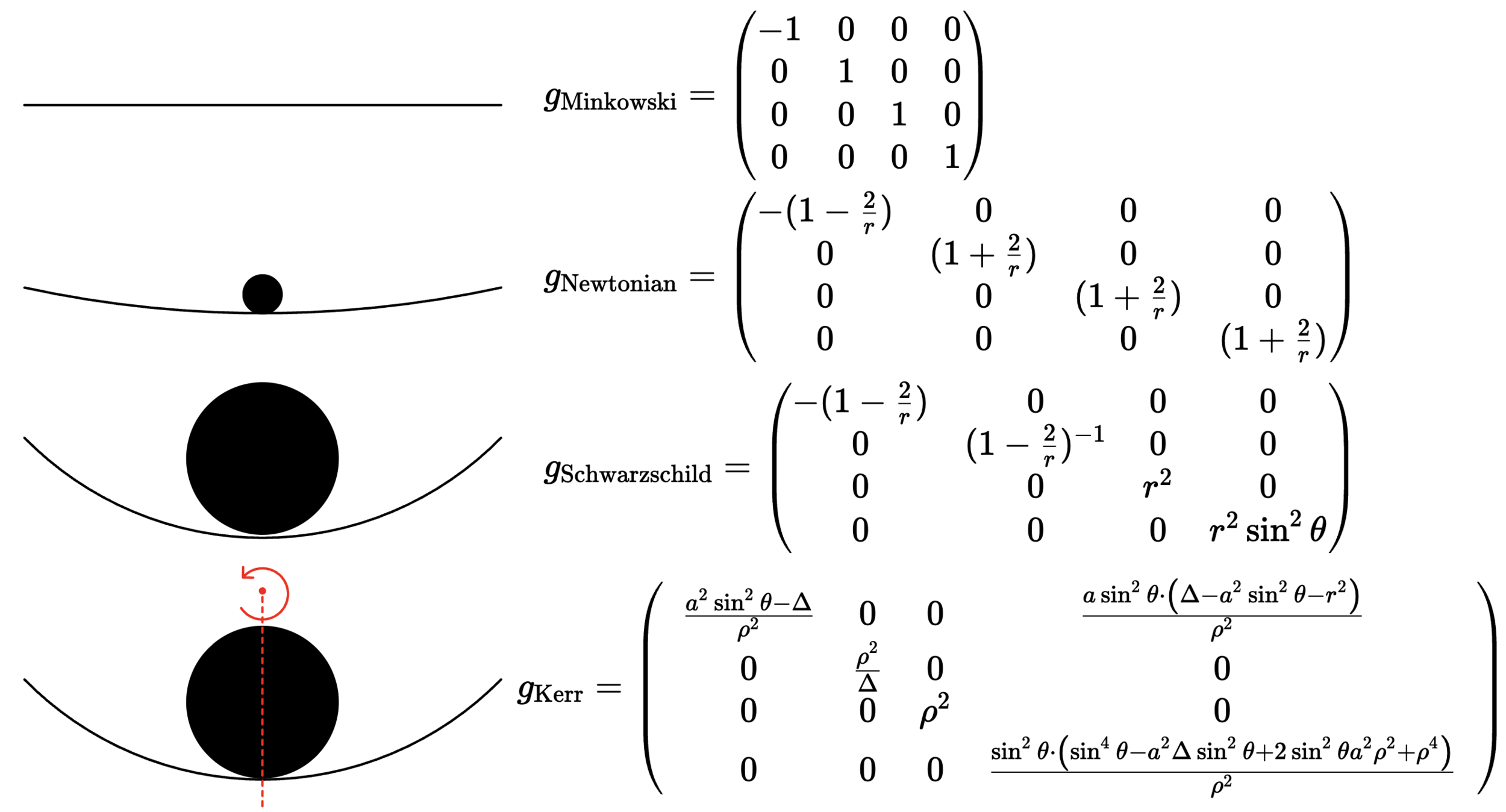
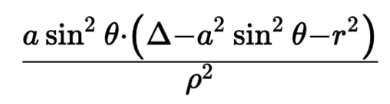
Approach


The Inverse Problem
GENERIC Formalism
Einstein's Field Equations
GENERIC Formalism
GENERIC Formalism
GENERIC Formalism
Synthetic Dissipation
Simulated Dissipation
Birkhoff's Theorem
Ricci Tensor
If a metric is a solution to
Einstein's Field Equations,
then R = 0
Approach


The Inverse Problem
GENERIC Formalism
Einstein's Field Equations
GENERIC Formalism
GENERIC Formalism
GENERIC Formalism
Synthetic Dissipation
Simulated Dissipation
Birkhoff's Theorem
Ricci Tensor
The Inverse Problem
GENERIC Formalism
Einstein's Field Equations
GENERIC Formalism
GENERIC Formalism
GENERIC Formalism
Synthetic Dissipation
Simulated Dissipation
Birkhoff's Theorem
Ricci Tensor
Approach


The unique spherically symmetric solution to Einstein's Field Equations is a static and asymptotically flat metric"
On the discovery of Birkhoff's theorem (Johansen, F Ravndal, 2005)
Metric
Christoffel Symbols
Riemann Curvature Tensor
Ricci Curvature Tensor
Ricci Scalar
Einstein's Field Equations: A Brief Intro
Metric
Christoffel Symbols
Riemann Curvature Tensor
Ricci Curvature Tensor
Ricci Scalar
Einstein's Field Equations: A Brief Intro
Coordinate-Dependent!
Metric
Christoffel Symbols
Riemann Curvature Tensor
Ricci Curvature Tensor
Ricci Scalar
Einstein's Field Equations: A Brief Intro
Coordinate-Independent!
Metric
Christoffel Symbols
Riemann Curvature Tensor
Ricci Curvature Tensor
Ricci Scalar
Einstein's Field Equations: A Brief Intro
Metric
Christoffel Symbols
Riemann Curvature Tensor
Ricci Curvature Tensor
Ricci Scalar
Einstein's Field Equations: A Brief Intro
Metric
Christoffel Symbols
Riemann Curvature Tensor
Ricci Curvature Tensor
Ricci Scalar
Einstein's Field Equations: A Brief Intro
Metric
Christoffel Symbols
Riemann Curvature Tensor
Ricci Curvature Tensor
Ricci Scalar
Einstein's Field Equations: A Brief Intro
Metric
Christoffel Symbols
Riemann Curvature Tensor
Ricci Curvature Tensor
Ricci Scalar
Einstein's Field Equations: A Brief Intro
0 for vacuum
solutions of
field equations!
Einstein's Field Equations: A Brief Intro
Approach


The Inverse Problem
GENERIC Formalism
Einstein's Field Equations
GENERIC Formalism
GENERIC Formalism
GENERIC Formalism
Synthetic Dissipation
Simulated Dissipation
Birkhoff's Theorem
Ricci Tensor
if Neural Network
predicts correct solution
to Einstein's Field Equations!



Neural ODE
Approach



Neural ODE:
Training Data

Approach



Neural ODE:
Training Data

Approach



Neural ODE:
Training Data
ODE Solver:

Approach



Neural ODE:
Training Data
ODE Solver:

Approach

Neural ODE:
Training Data
ODE Solver:
BFGS Optimizer:
Neural ODE:
Training Data:
ODE Solver:
BFGS Optimizer:
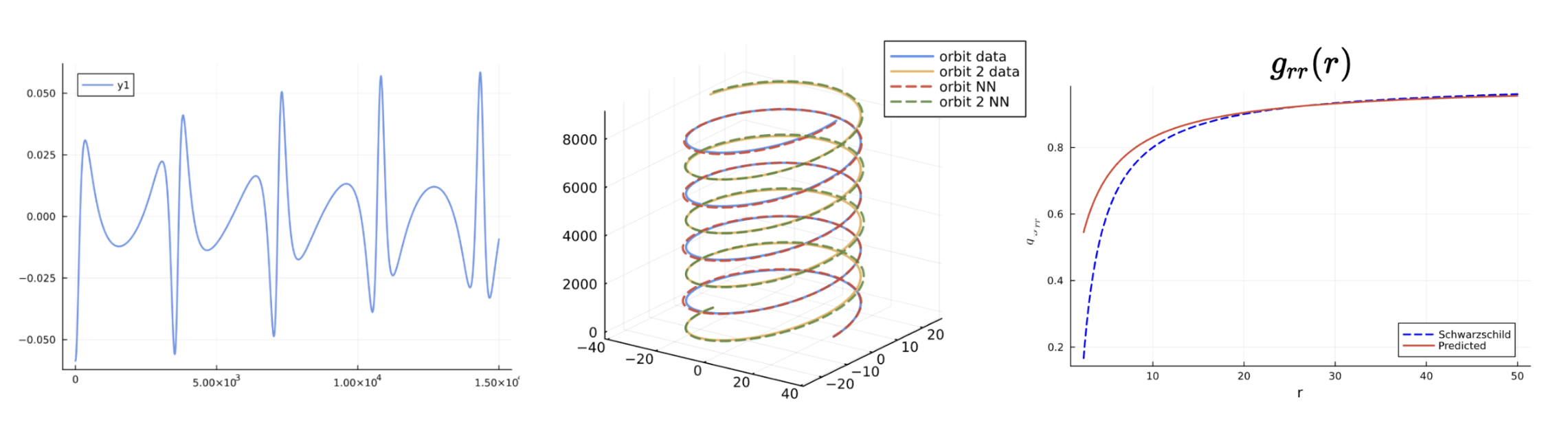
Results


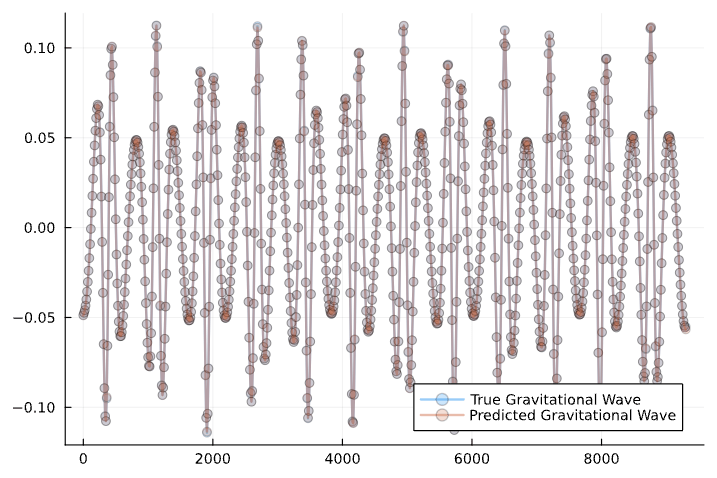
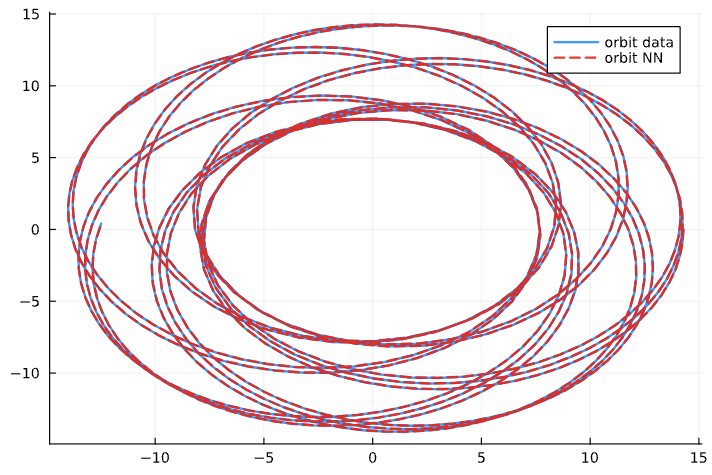
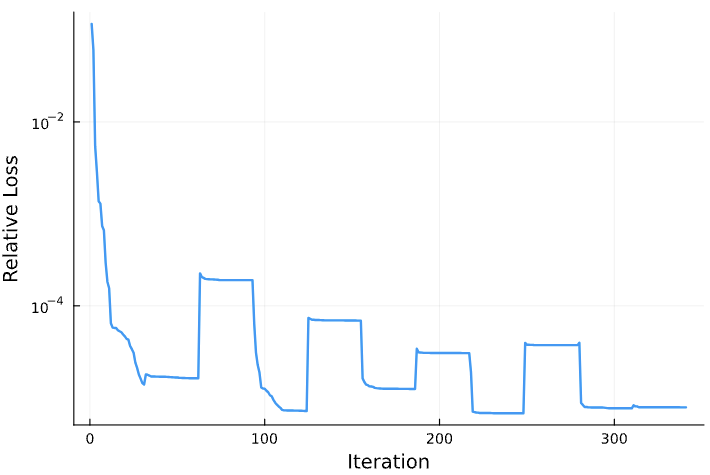
Results


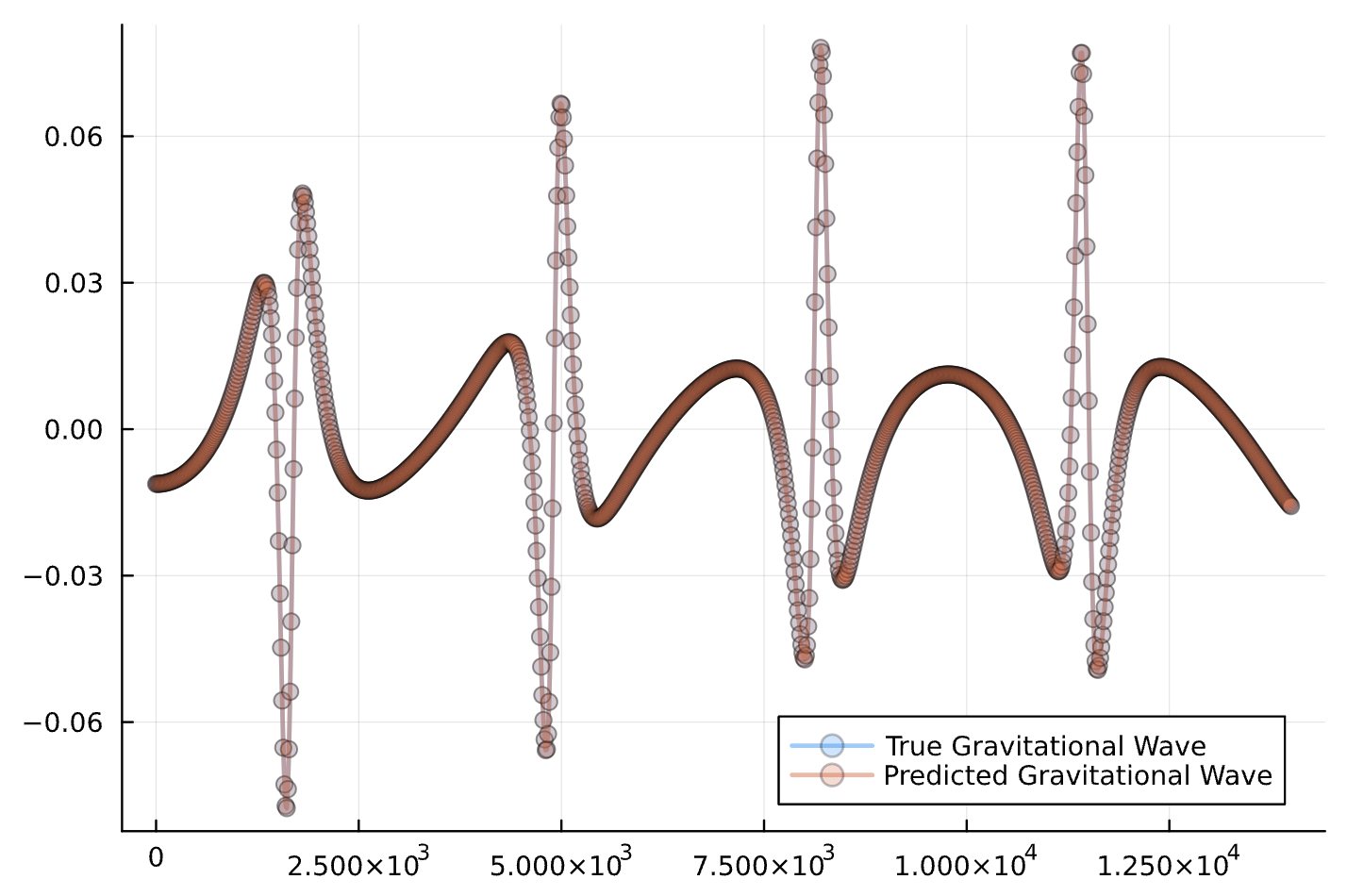
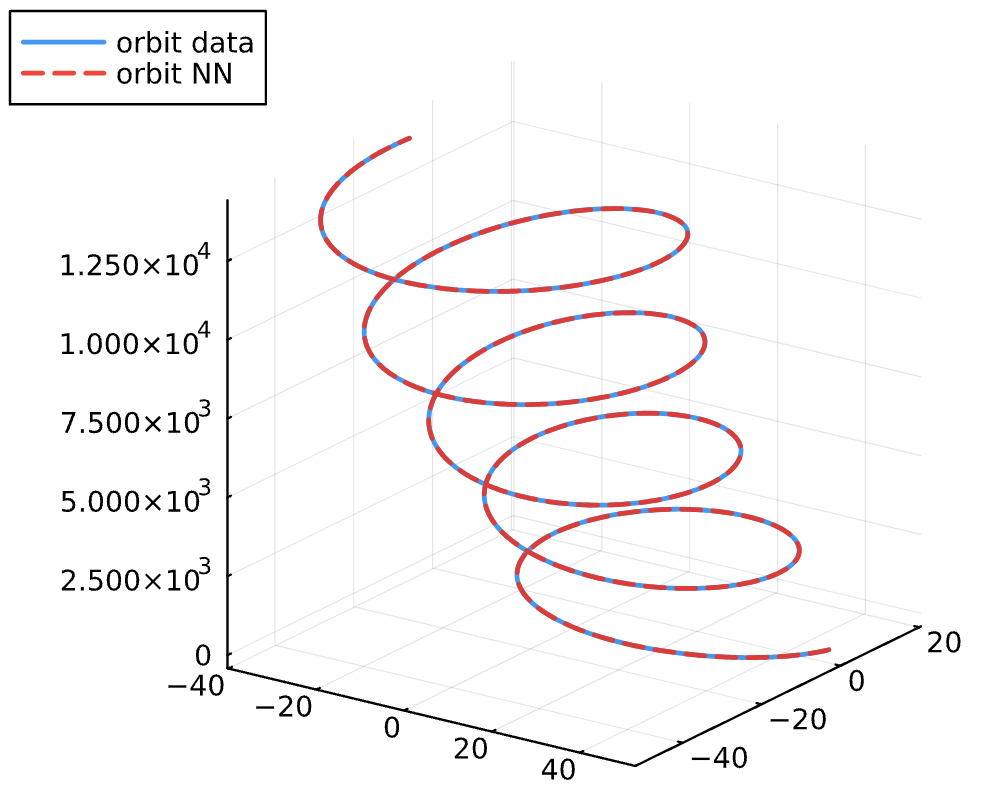
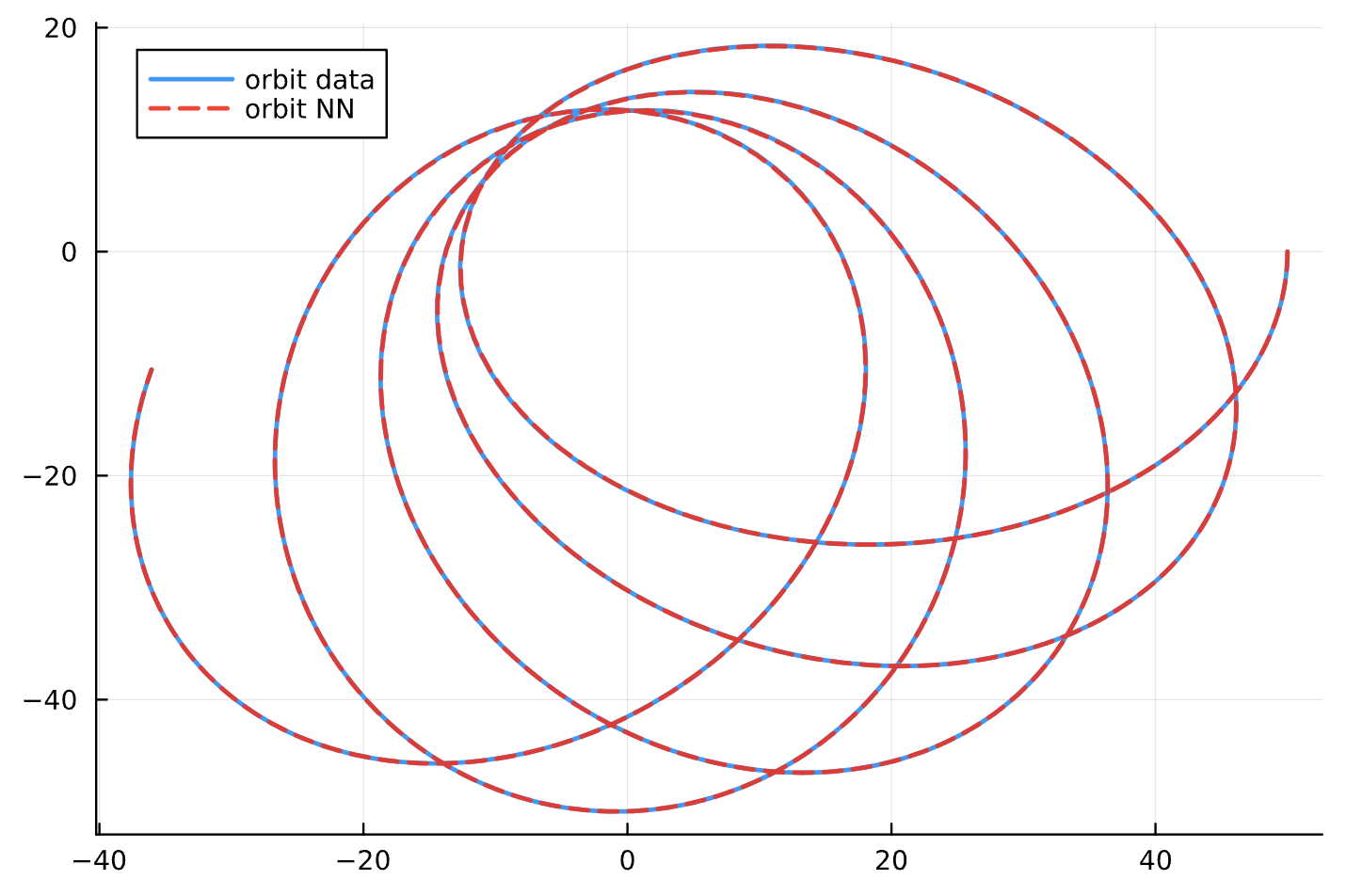
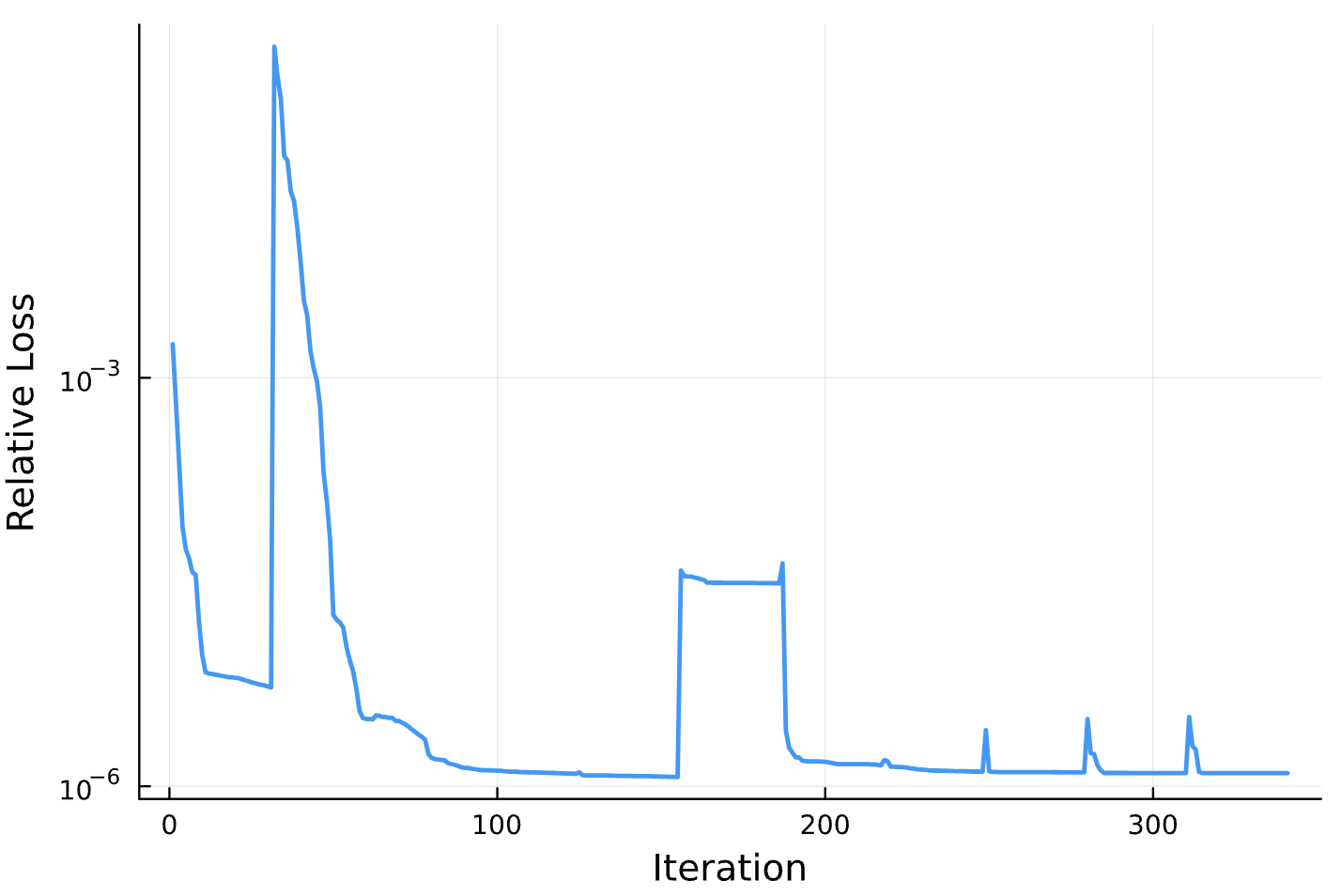



Results







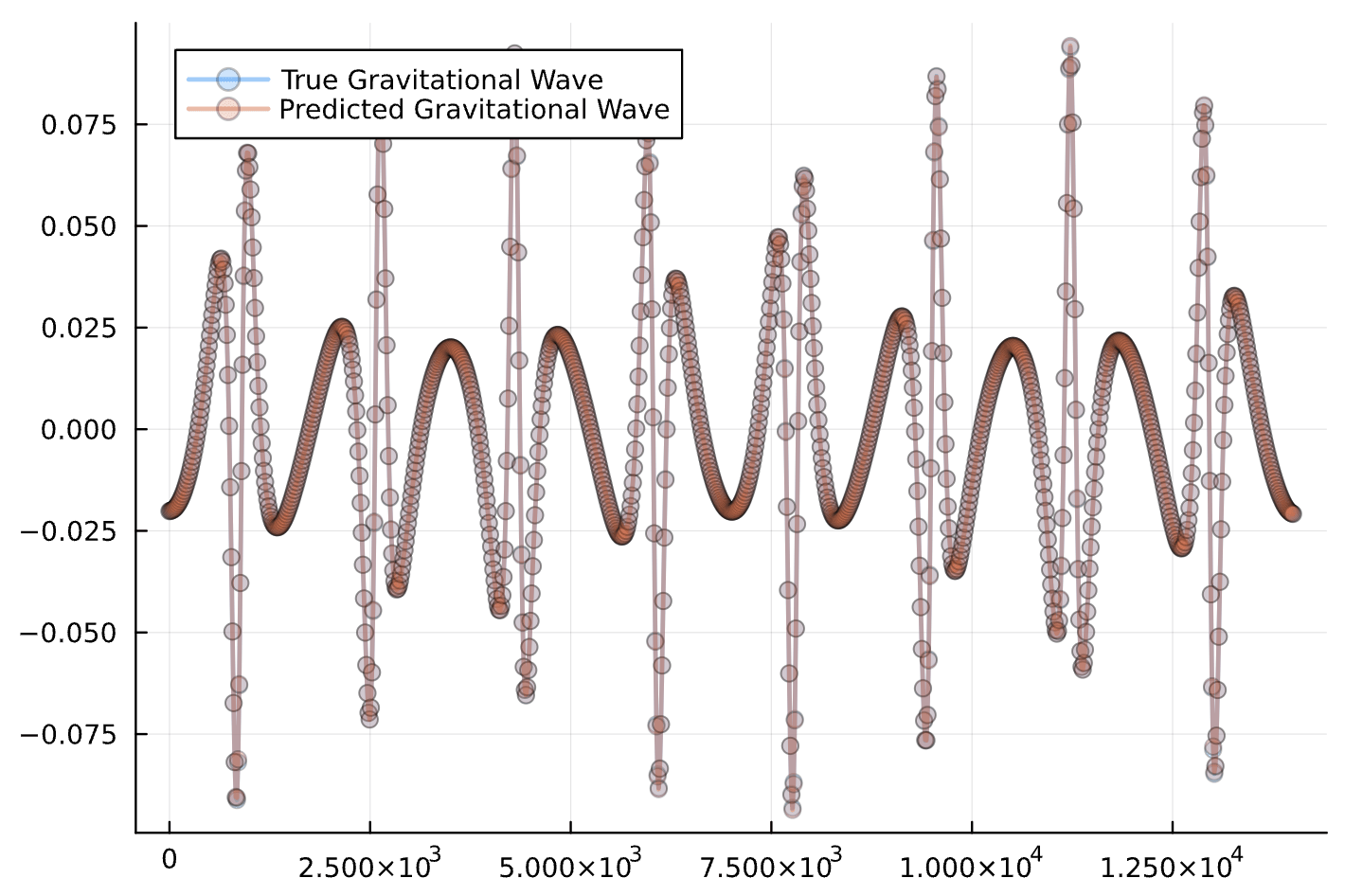
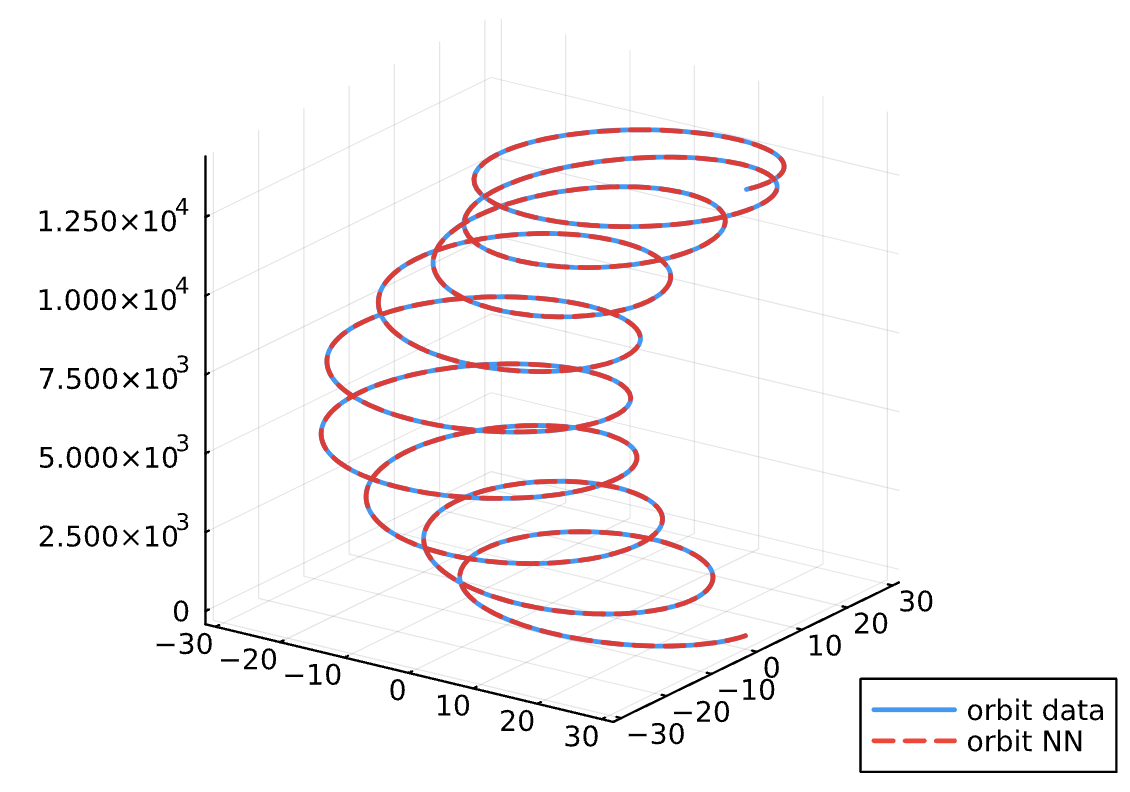
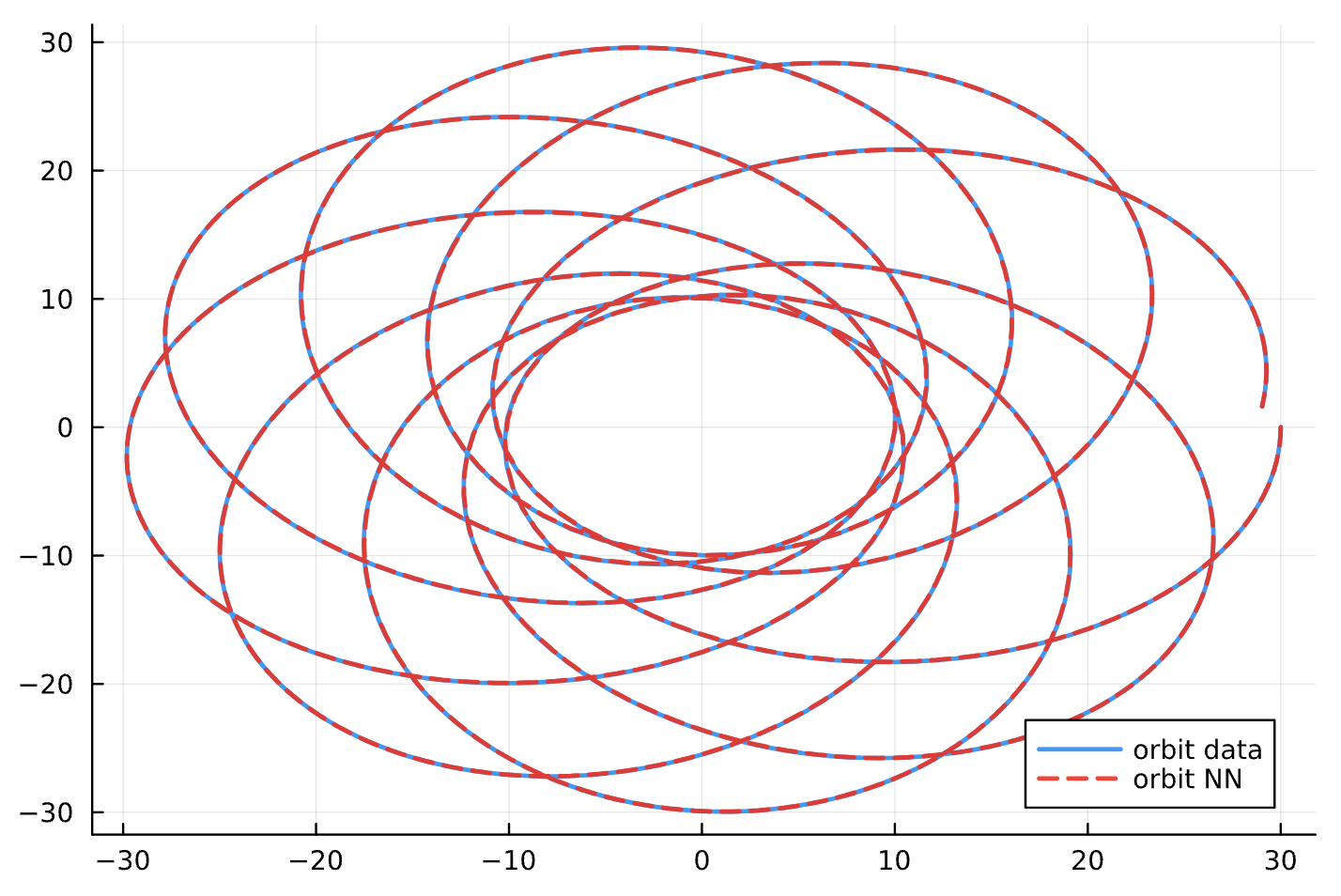
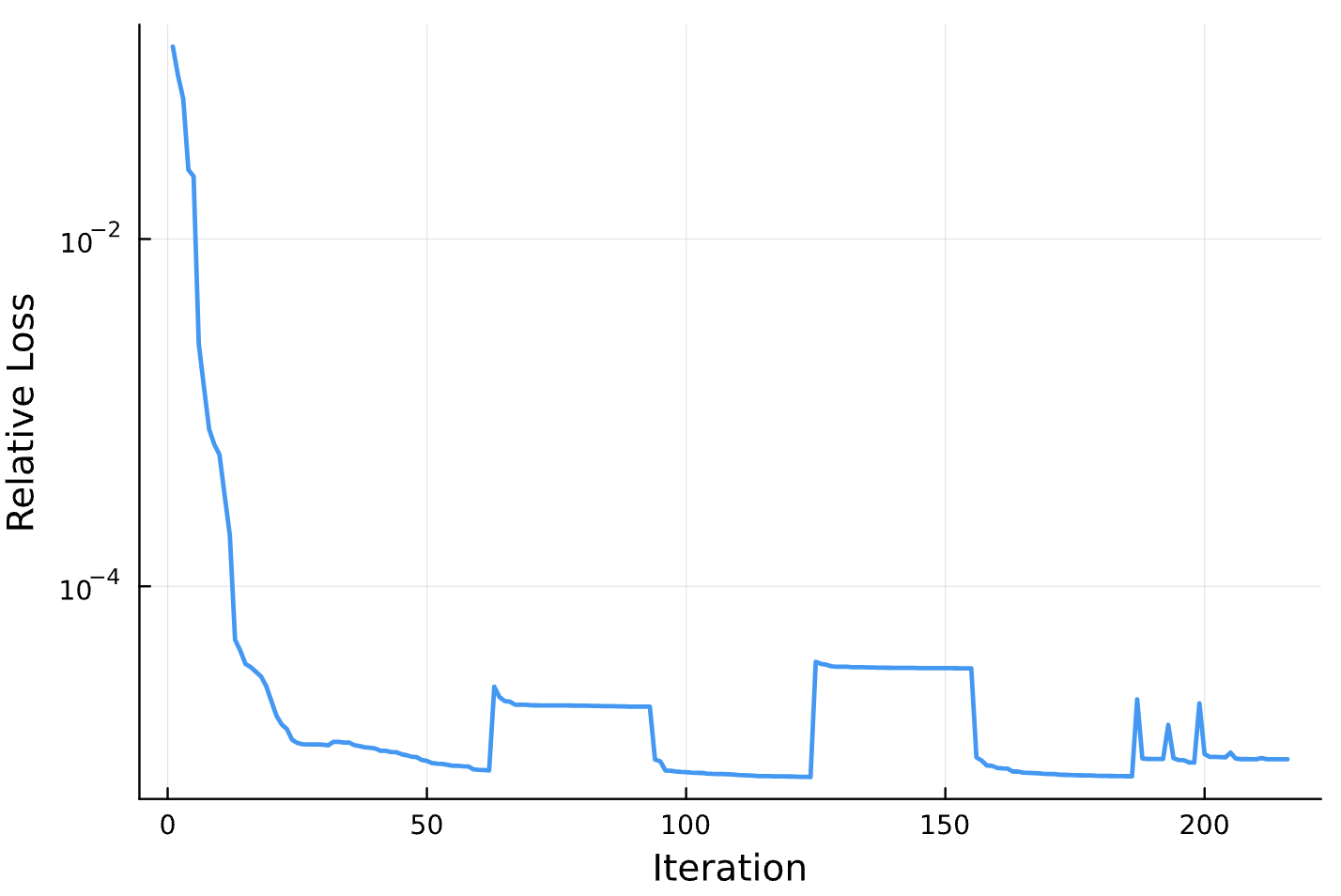
Results











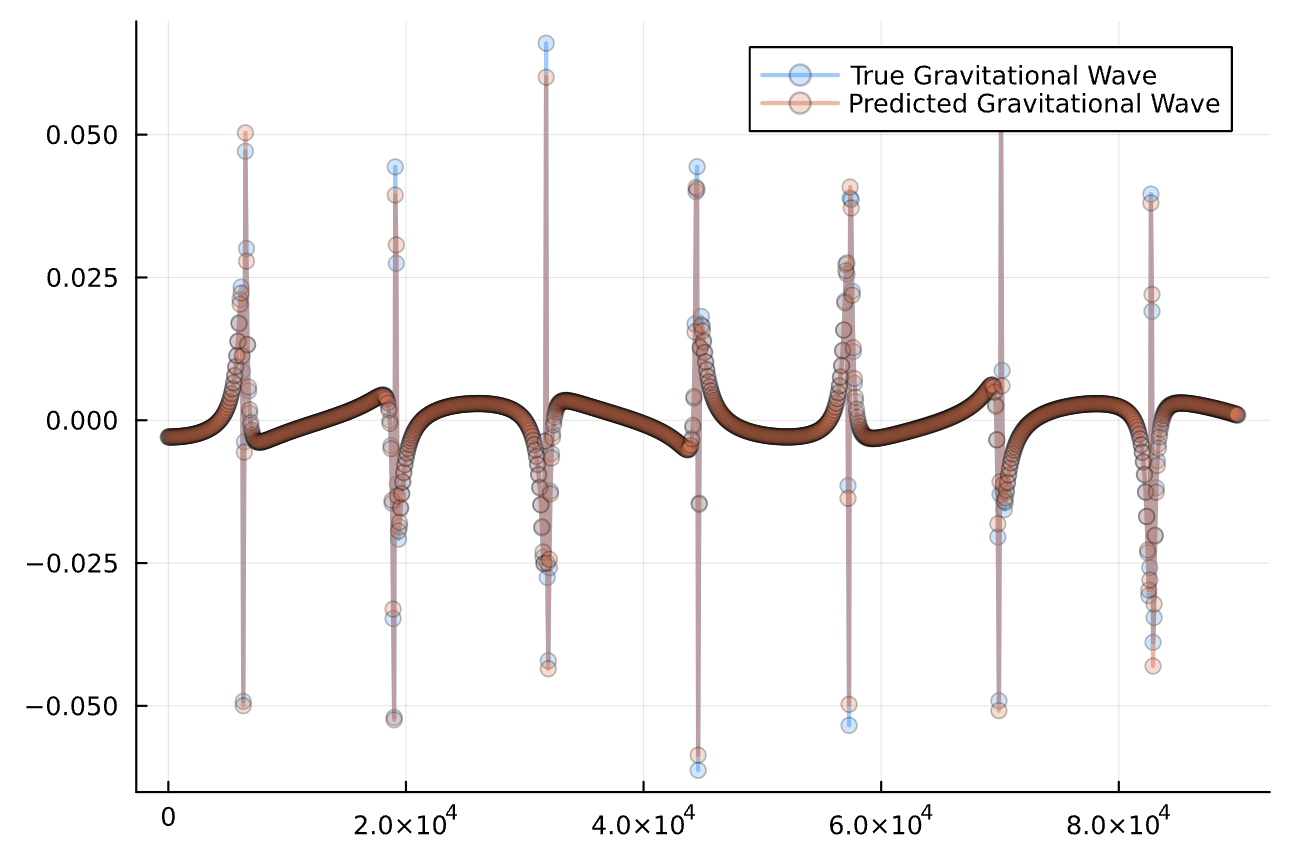
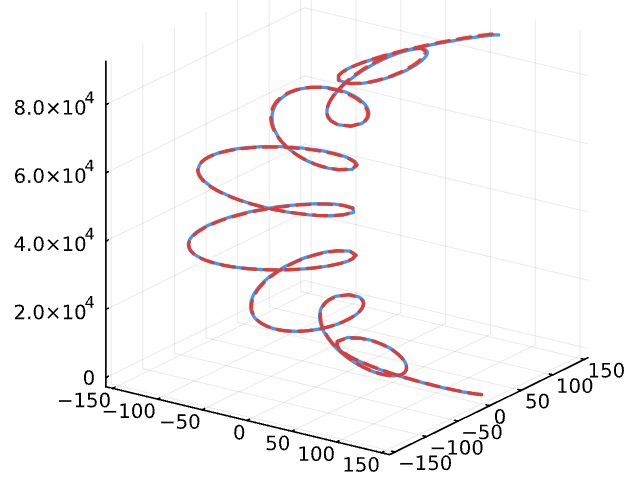
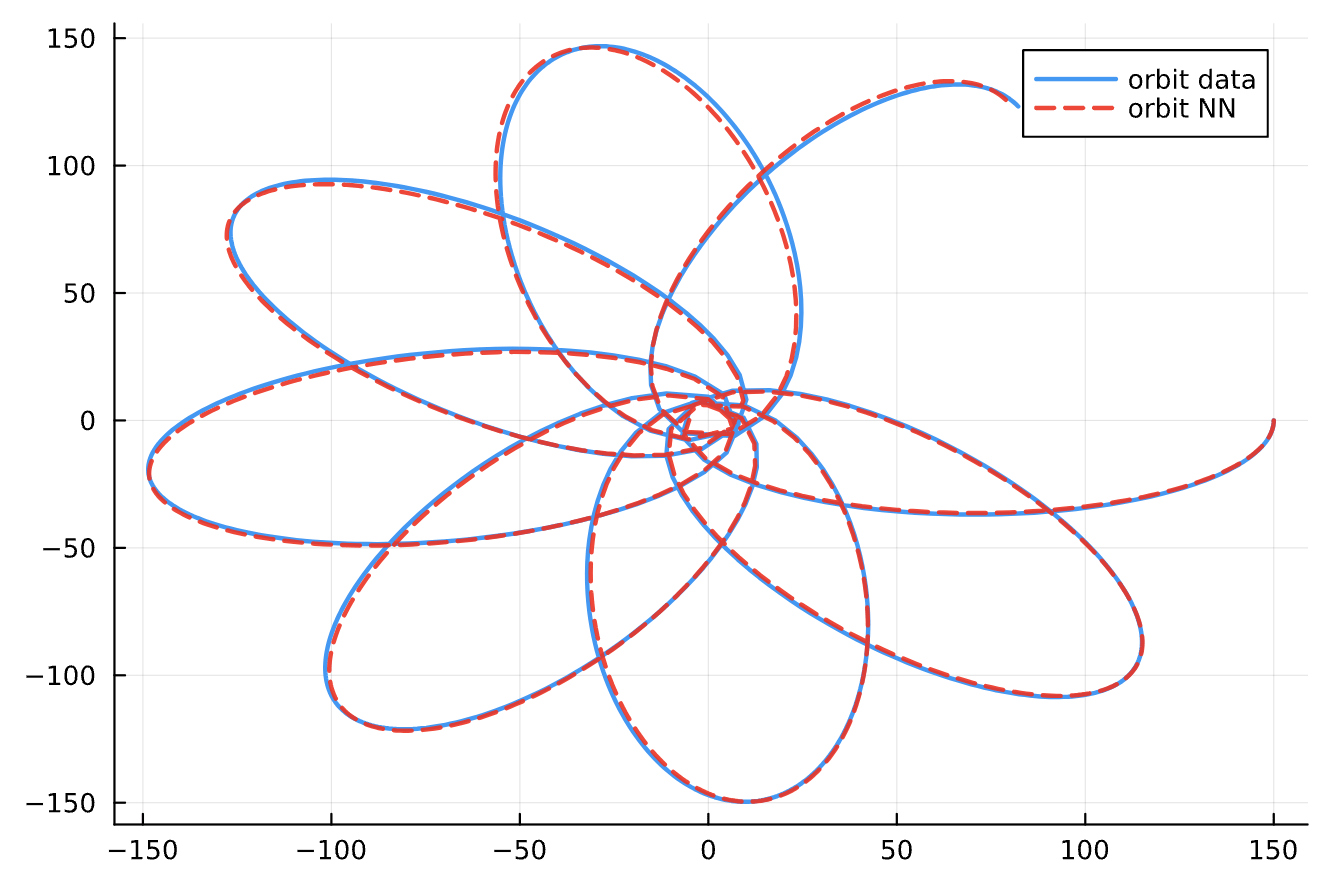
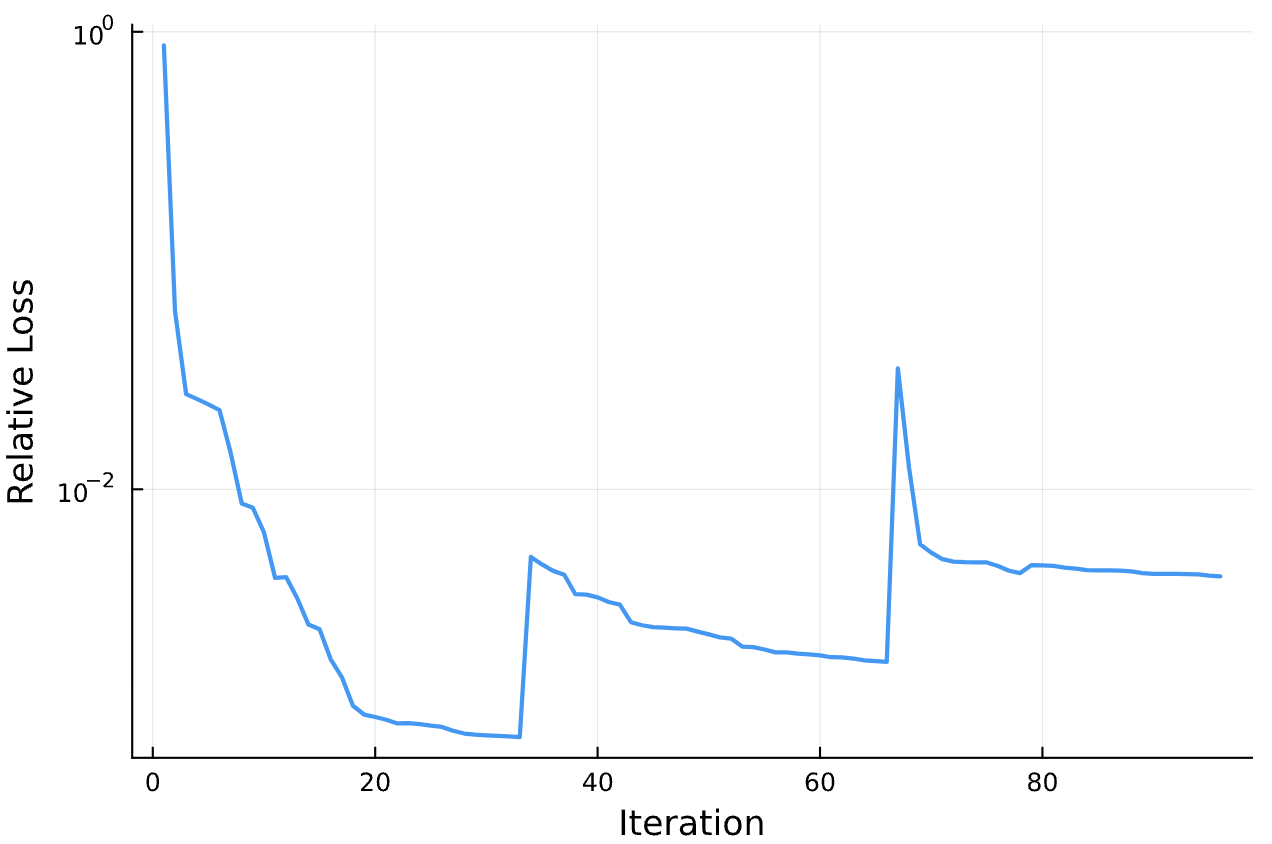
The Inverse Problem
GENERIC Formalism
Einstein's Field Equations
GENERIC Formalism
GENERIC Formalism
GENERIC Formalism
Synthetic Dissipation
Simulated Dissipation
Birkhoff's Theorem
Ricci Tensor
Results


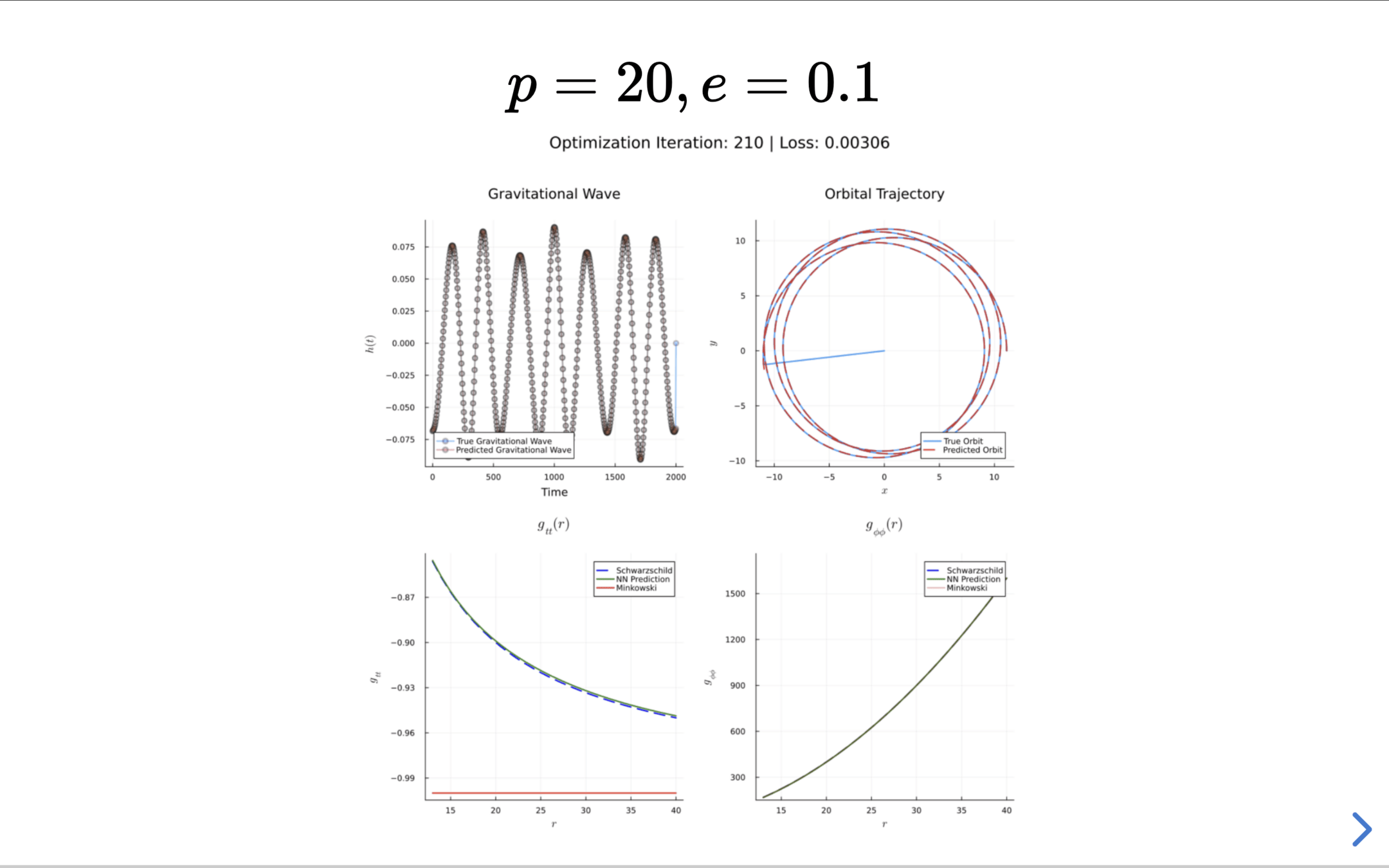
The Inverse Problem
GENERIC Formalism
Einstein's Field Equations
GENERIC Formalism
GENERIC Formalism
GENERIC Formalism
Synthetic Dissipation
Simulated Dissipation
Birkhoff's Theorem
Ricci Tensor


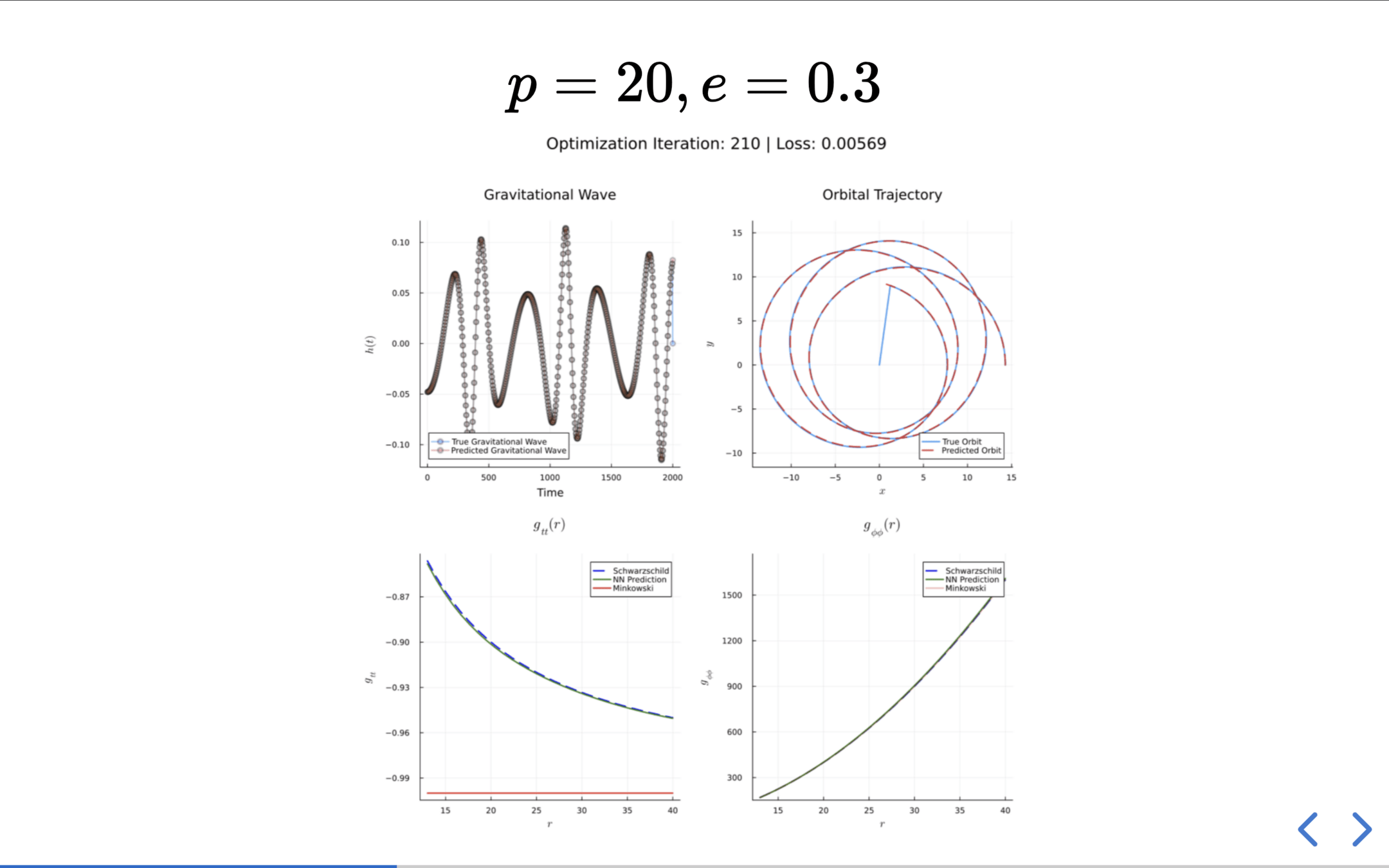
Results
The Inverse Problem
GENERIC Formalism
Einstein's Field Equations
GENERIC Formalism
GENERIC Formalism
GENERIC Formalism
Synthetic Dissipation
Simulated Dissipation
Birkhoff's Theorem
Ricci Tensor


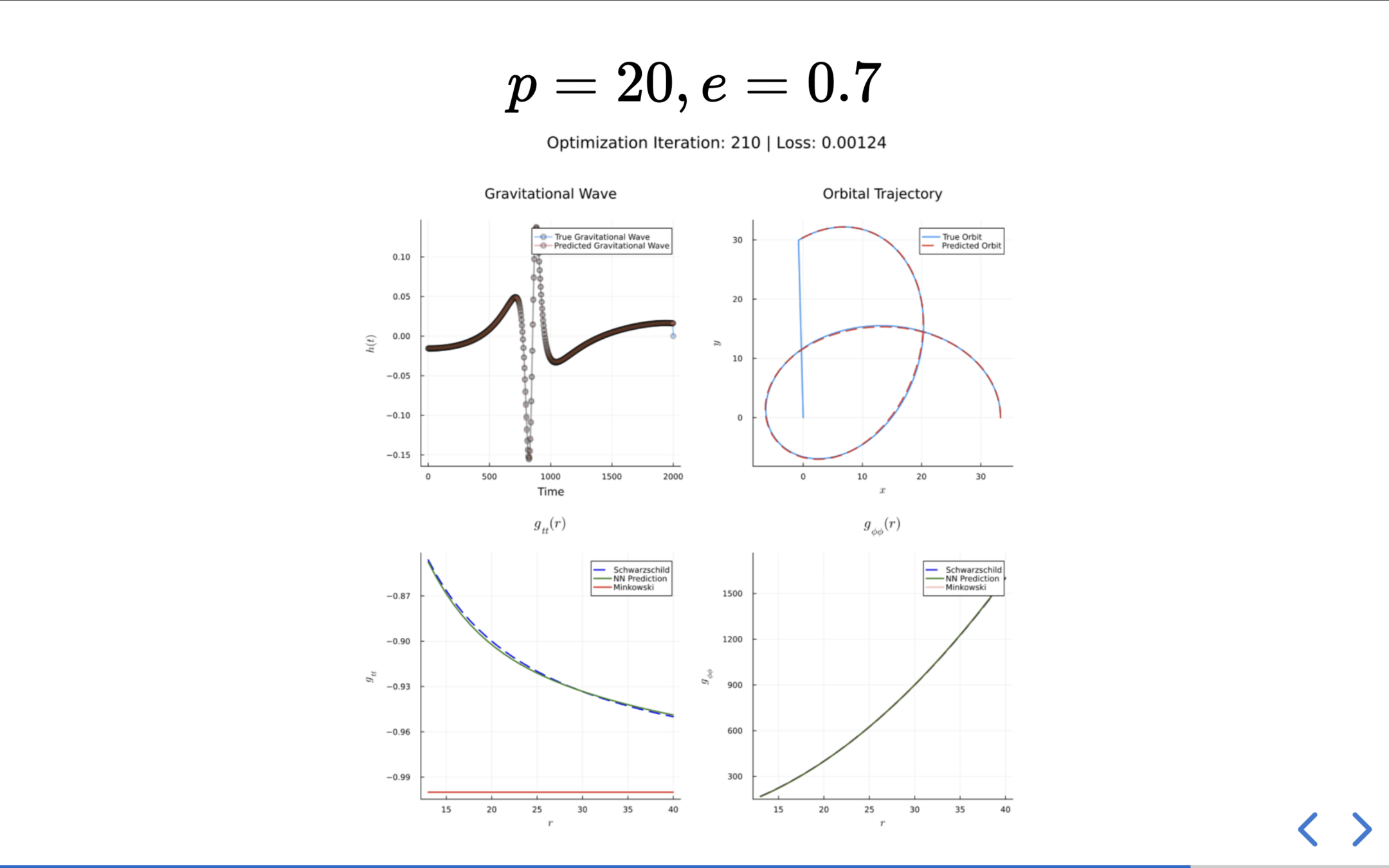
Results


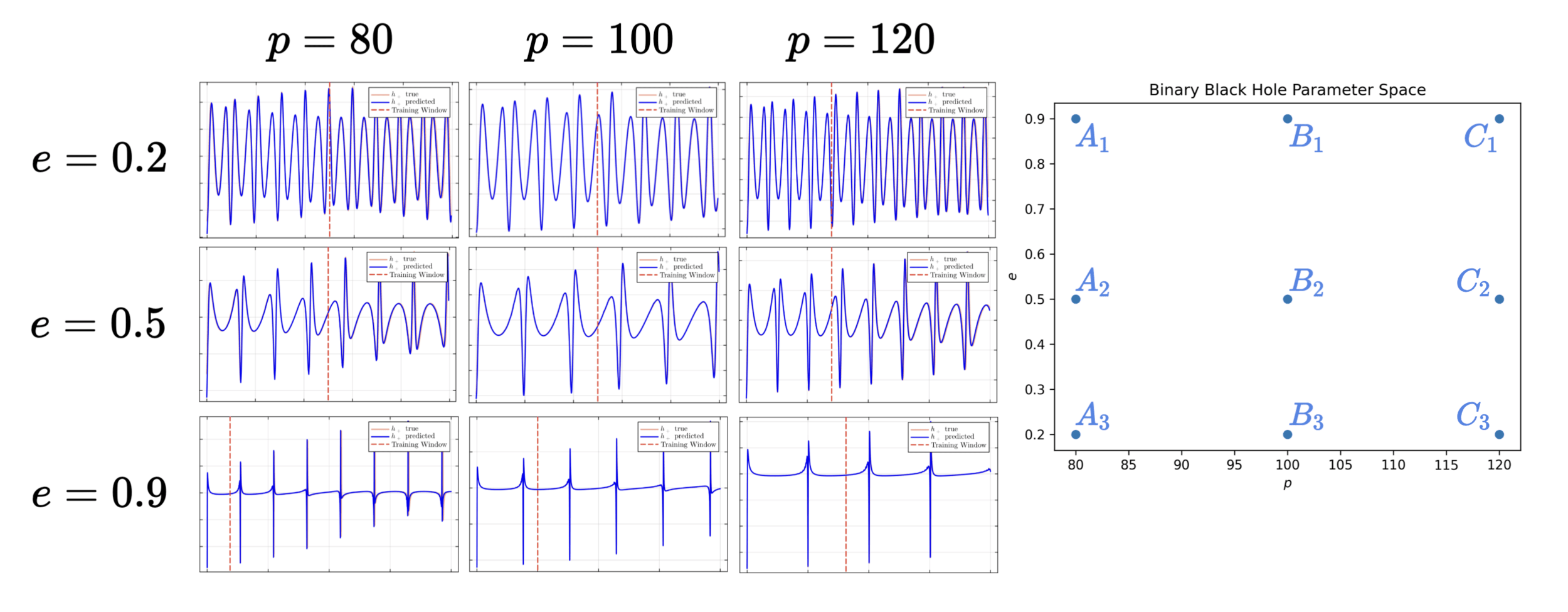
Results


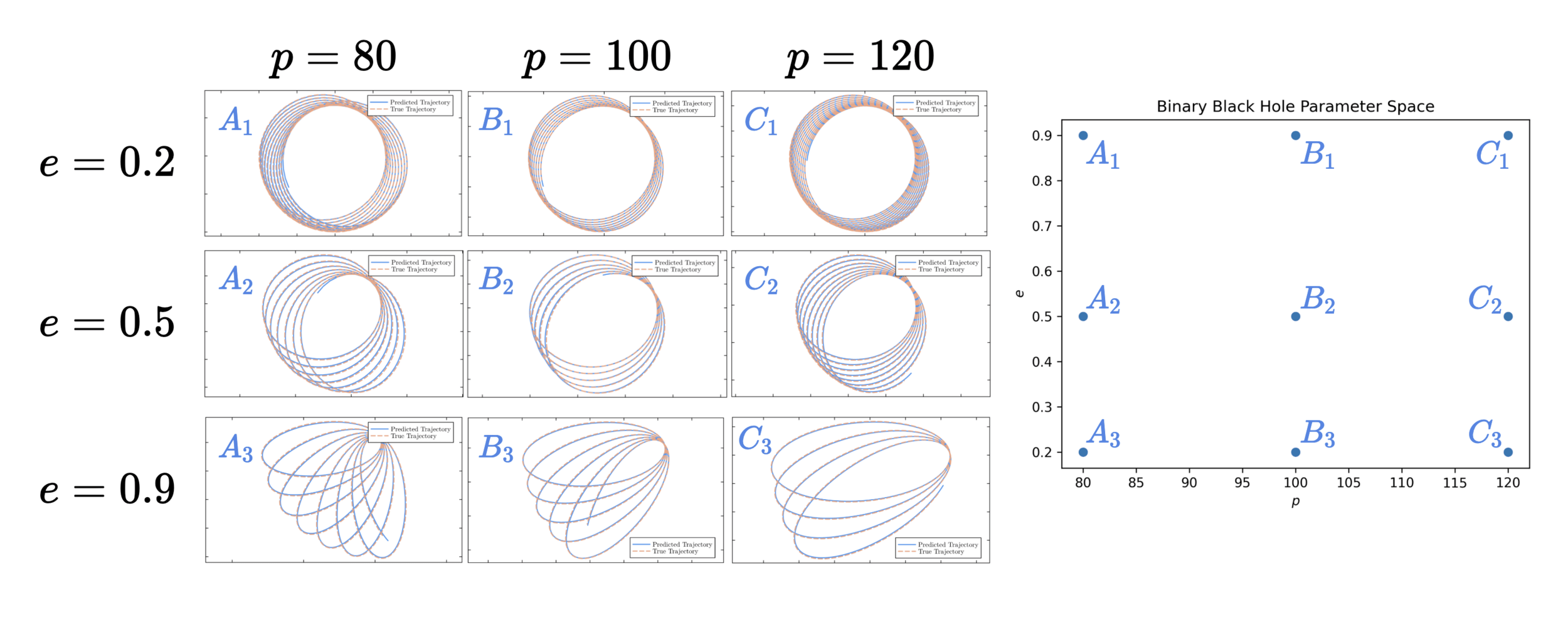
Results
The Inverse Problem
GENERIC Formalism
Einstein's Field Equations
GENERIC Formalism
GENERIC Formalism
GENERIC Formalism
Synthetic Dissipation
Simulated Dissipation
Birkhoff's Theorem
Ricci Tensor

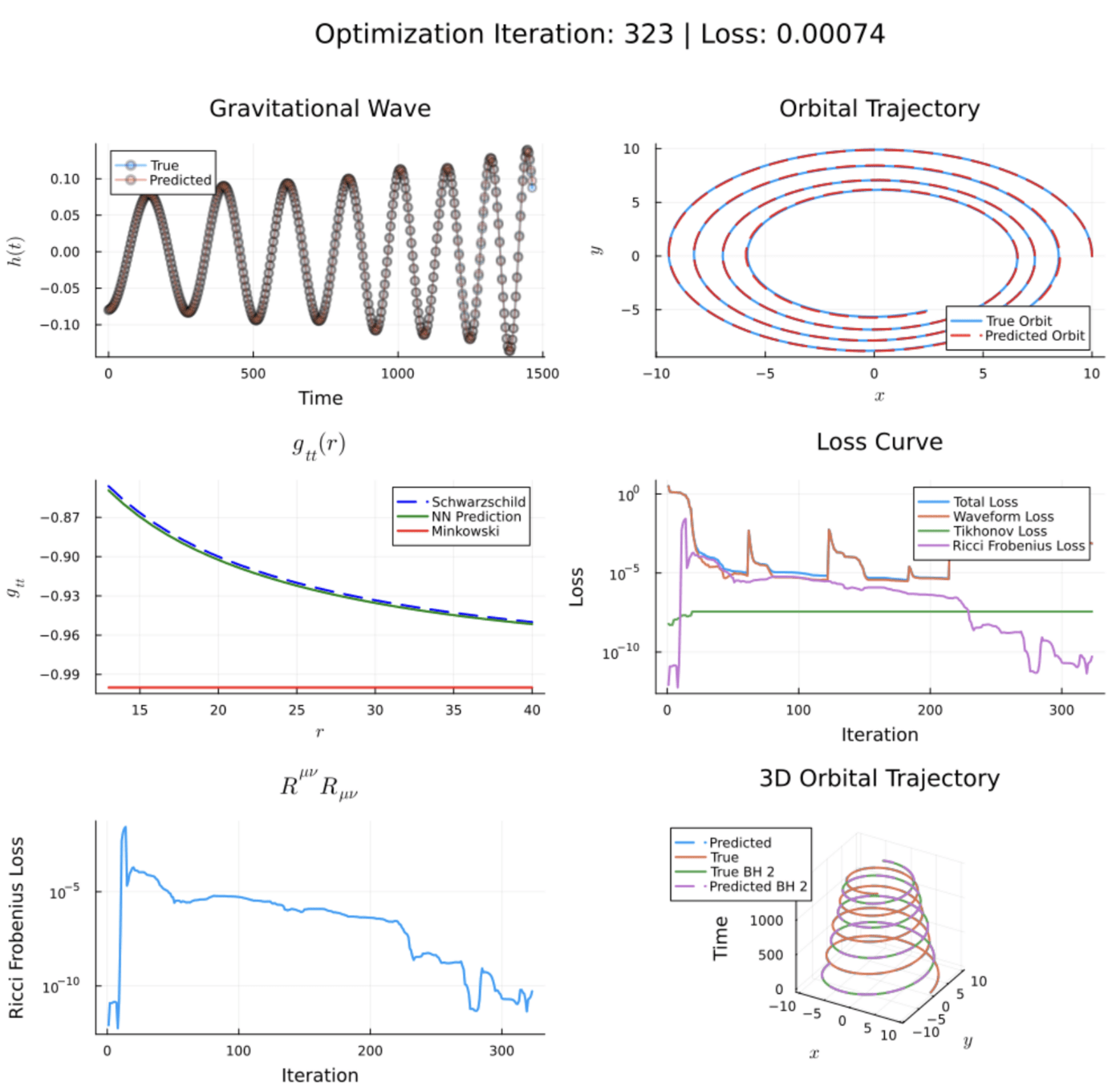
Results


Results



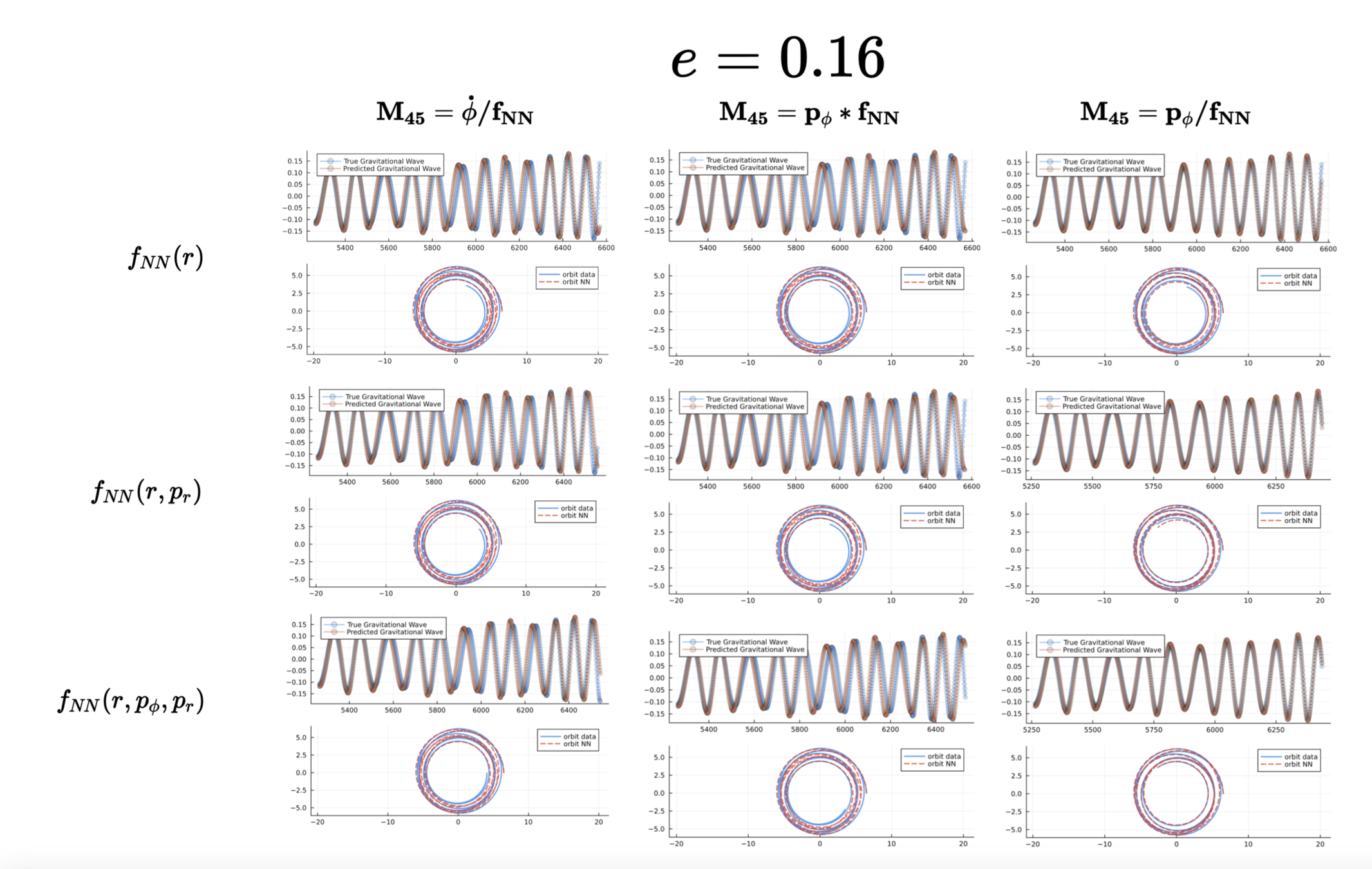
Results


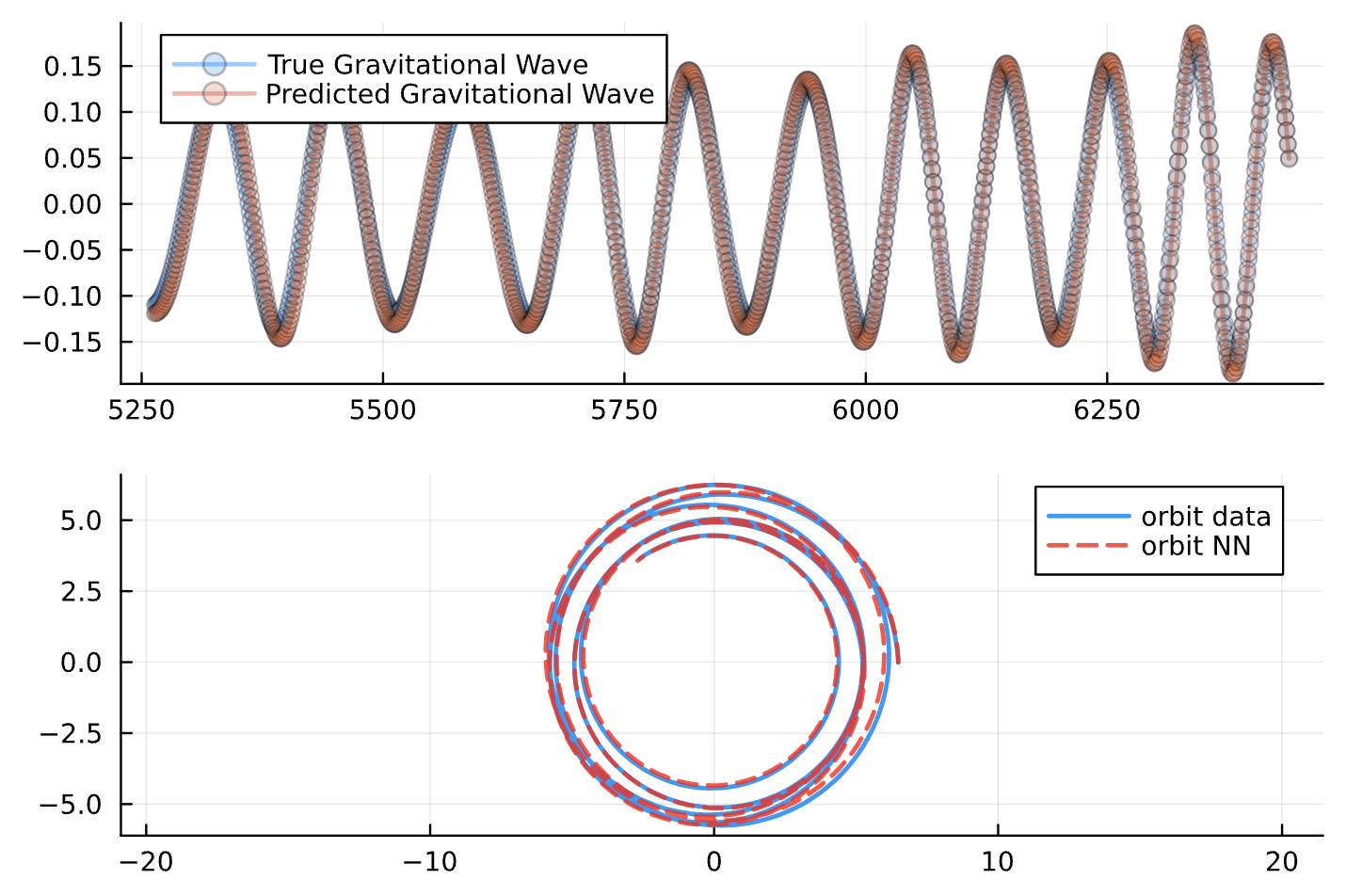
Results


Summary





Summary
Conservative Dynamics: We created a NN which can learn solutions to Einstein's Field Equations (Schwarzschild Metric) from only gravitational waves
Dissipative Dynamics: NN can learn both conservative and dissipative dynamics of a binary black hole inspiral for the synthetic dissipation case.


Future Work
Conservative Dynamics: Extend to rotating, Kerr black holes, which are not spherically symmetric
Dissipative Dynamics: Test Neural ODE on SXS waveforms from NR simulations and on real, observed LIGO data
Thanks!


Black Holes | JMM 2026 Talk
By Ref Bari
Black Holes | JMM 2026 Talk
- 60



